
The Super Efficient Energy Station (SEES) system, designed to maximize energy efficiency, combines innovative energy-saving equipment with advanced system optimization. The construction and implementation of SEES involve multiple stages, from equipment selection to system design, optimization, construction, and operation. Ensuring consistent operational efficiency is a challenge in such complex systems. However, BROAD goes beyond being an equipment manufacturer or system designer, positioning itself as a critical investment operator. This approach allows BROAD to offer expertise in precise control and comprehensive management at every stage of the project.
Project Highlights
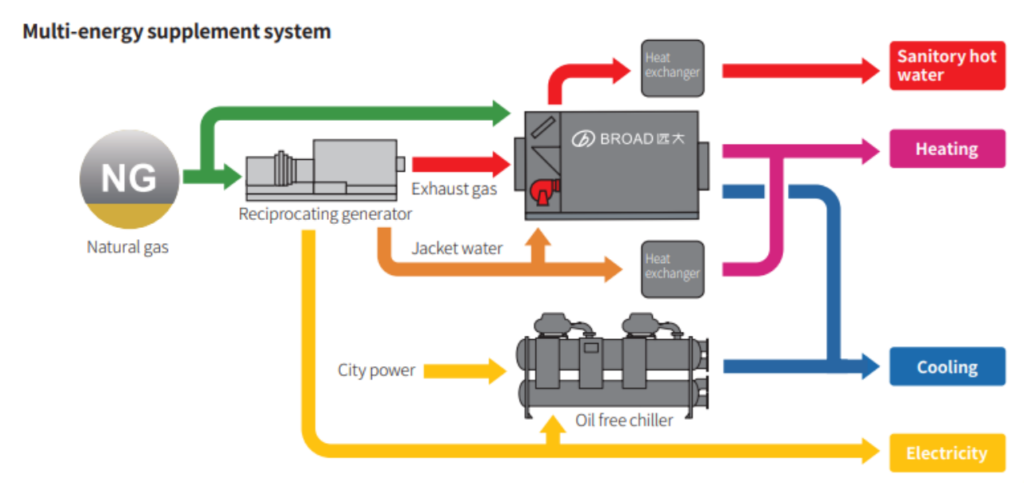
At Hunan Women’s and Children’s Hospital (HWCH), BROAD has taken a holistic approach to the energy station. The company invested in, designed, constructed, and currently operates the station following SEES standards. The energy station provides services like cooling, heating (including hot water), electricity, and steam for the hospital’s first phase. It integrates a variety of energy-saving technologies such as Combined Cooling, Heating, and Power (CCHP), oil-free chillers, condensing heat recovery direct-fired chillers, and condensing direct-fired boilers (vacuum boilers). Notably, three of these technologies are featured in the “National Key Energy-Saving Low-Carbon Technology Promotion Catalog.”
BROAD’s operational strategies ensure the energy station operates safely, stably, and efficiently. These strategies are fine-tuned based on the characteristics of the equipment and local energy pricing, optimizing overall energy consumption.
Project Overview
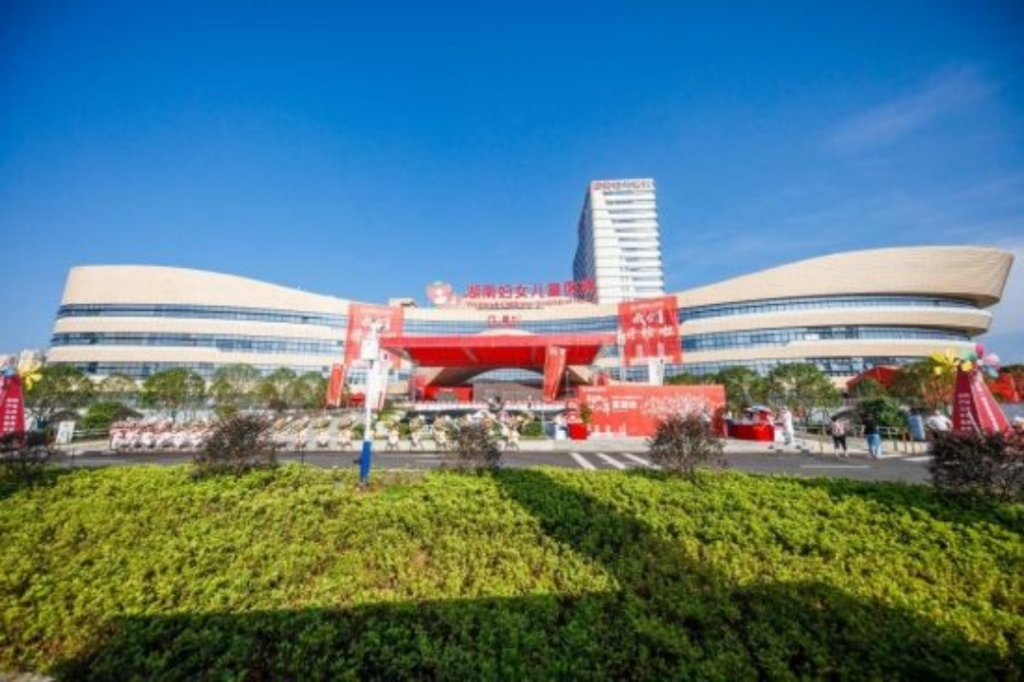

Hunan Women’s and Children’s Hospital, located in Changsha, China, is a 3A-class medical facility designed to meet the highest healthcare standards. Built to comply with international JCI standards, the hospital is a model of high-quality construction, operations, and patient services, offering a smart healthcare experience enhanced by life-cycle butler service.
The hospital covers an area of 86,600 square meters, with a planned construction area of 400,000 square meters and a capacity of 1,500 beds. The first phase spans 150,000 square meters, including a medical complex and logistics center. The main hospital tower reaches 19 stories above ground, with two underground levels.
Energy and Load Demands

The hospital’s main functions include outpatient services, medical technology areas, wards, neonatal rooms, and laboratories, all of which demand precise climate control. The design parameters ensure comfortable environmental conditions, maintaining summer temperatures between 23-25°C and winter temperatures between 22-24°C, with humidity levels maintained between 40-60%. The hospital’s total cooling load is 17,807 kW, while the heating load reaches 13,476 kW. Peak hot water consumption is 161.6 m³ per day, with a maximum hourly usage of 23.95 m³/h.
Key Equipment and Technologies


- CCHP System: The Combined Cooling, Heating, and Power system generates 1,000 kW of power with an efficiency rate of 41%. The system repurposes waste heat for free cooling, heating, and sanitary hot water. With a cooling capacity of 853 kW and heating capacity of 514 kW, the CCHP system operates with a cooling efficiency of 99% in summer and 93% in winter.
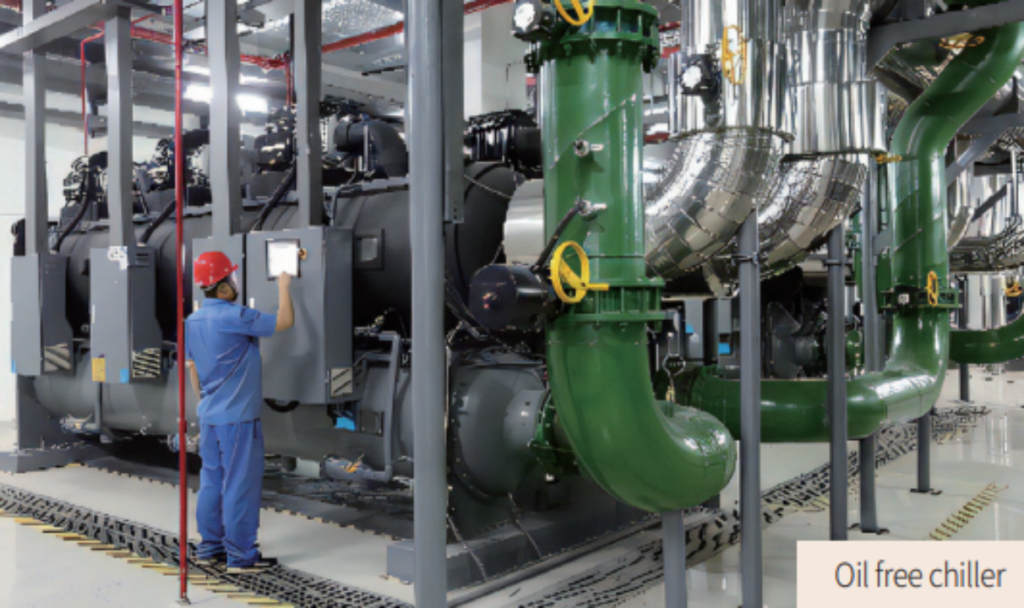

- Oil-Free Chillers: The energy station is equipped with two oil-free chillers that provide cooling capacities of 4,200 kW and 4,885 kW, respectively. With an IPLV (Integrated Part Load Value) exceeding 10, these chillers are 40% more efficient than conventional models. The oil-free operation reduces maintenance costs and extends the compressor’s lifespan by up to 30 years.

- Exhaust Heat Exchanger: This system preheats sanitary and boiler hot water, reducing exhaust gas temperatures to 40-50°C. By increasing the natural gas utilization rate to 103%, the system lowers operating costs and minimizes emissions from flue gases.

- Condensing Heat Recovery Chiller: This technology captures condensation heat from cooling processes to generate sanitary hot water, reducing energy consumption by over 50% compared to conventional chillers and boilers. In some cases, the system can even provide hot water for free.
Conclusion
The SEES system at Hunan Women’s and Children’s Hospital showcases how cutting-edge energy technologies can revolutionize healthcare efficiency. By integrating advanced systems like CCHP, oil-free chillers, and heat recovery technology, BROAD has created a model of sustainable, cost-effective energy management that sets a new standard for hospital energy stations. This approach not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes the hospital’s environmental impact, contributing to a more sustainable future for healthcare infrastructure.
